1.
a. People will pay 8.2 cents per pound more for beef that is 90% lean than for beef that is 10% fat. What specific kind of cognitive bias is this an example of? (1 mark)
A framing bias. This was discussed in class and announced as guaranteed midterm question.
b. Studies have shown that people who use gestures when they talk may communicate more effectively that people who don’t use gestures. Explain how Multiple Resource Theory might predict this result.
n
2. A worker cleaning an auxiliary building at a power plant catches his shirt on a breaker. In pulling it free, he activates the breaker, shutting off current to the control rods in the reactor. The reactor shut down automatically and it took 4 days to bring it up again. Explain why this is an accident caused by system characteristics.
This example was used in the lecture in class.
It is a system accident because
Marking: This would be a two mark question with one mark for each point.
3. Mary sends out this message “I am writing a midterm today” in two different ways, once using Morse Code, and then using email. (Morse code is way of communicating that has only two keys, dash and dot, and alphabet letters are made by combinations of three dashes or dots. Assume Mary is very proficient at both Morse code and typing. Which method will she likely send out the message the fastest? Why? Which method will she have the fastest keystroke/second speed? Why?
Total message will be faster typing – due the Decision Complexity Advantage. because more information is being sent per keystroke. I was picky and wanted the specific law named as well as the explanation for 1 mark.
Keystroke speed will be faster with Morse Code because of the Hick Hyman law. The HH law states that decision speed is faster with fewer decisions to be made, in this case, 2 keys rather than 26. Again state the law.
Not accepted: Fitts law. There is no information on target width or distance to target (amplitude) so you really can’t solve this problem with Fitts law.
marking: (4 marks, 2 for the choice of method and 2 for the reasons why)
4. Use Action Cycle to explain what happened in the case study “the Lost Cord”.
Goal: monitor girl’s condition
Intention: monitor her heart using the EKG machine
Sequence of Actions: tape electrodes to girl’s chest , run lead across mattress, plug into heart monitor machine
Actions: physically doing the above sequence but plugs into IV pump instead
World: Girl connected to IV pump and electricity into girl.
Perception: seeing girl get electrocuted
Interpretation: wrong amount of electricity into girl, wrong piece of equipment.
Evaluation: could not monitor girl’s condition , girl dead ; goal not achieved * you need to tie back to goal
marking: 8 marks, 1 for each level of the cycle (1/2 mark for labels and ½ mark for explanation)
5. In Set Phasers on Stun, is there a gulf of evaluation? And why?
You are expected to use the human action cycle directly. There is no information on the state of the world , there is no information to perceive, there is no information to evaluate.
marking: 3 marks
Propose one solution in each category
- making an error reversible
- making an error visible
- making an error impossible
marking: 3 marks.
Reversible: Allow Mary Beth to look at her entry and revise it before starting treatment
Visible: Warning that the set level may be too high
Impossible: Prevent the device from emitting fatal levels of radiation under all circumstances.
(there may be some other solutions here)
Bob is in his final year of high school. He is interested in 2 universities and is trying to decide which one to go to. The universities differ on certain attributes. Use Multi-attribute utility theory to determine which university Bob should go to.
| Attribute | Utility of the Attribute | U1 score | U2 score |
|
|
|
|
|
| Social life | 10 | 2 | 8 |
| Reputation | 3 | 10 | 3 |
| Closeness to home | 5 | 3 | 7 |
| Sports teams | 9 | 4 | 5 |
| Quality | 7 | 8 | 4 |
| SCORE | 157 | 197 |
U1=2*10+3*10+5*3+9*4+7*8=20+30+15+36+56= 157
U2= 8*10+3*3+7*5+5*9+4*7=80+9+35+45+28=197
Bob should go to University#2
Marks 2 for the correct method
2 for the correct scores
1 for the correct decision.
7. (7 marks) Explain what “Automation Complacency” is. Describe its effect on human operators. Give an example of automation complacency from the film “Why Planes Crash”.
From the notes, automation complacency refers to a situation where operators overtrust the automation. (1 mark)
They fail to monitor it vigilantly enough and
become less aware of the state of the system
they are slower to detect problems
and less able to intervene in a problem (de-skilling) (4 marks)
An example from the film is when the pilots focus on the burned out lightbulb. They assume the plane is in autopilot and stop monitoring the altitude. By the time they realize the plane has descended too much they are unable to intervene. (2 marks)
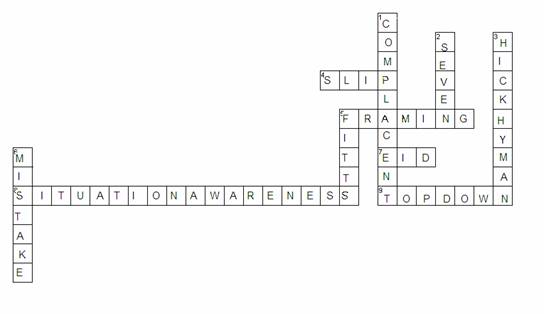
8. (10 marks – 1 per word) Solve the Human Factors Crossword Puzzle
Across
4. error with correct intention and wrong action
5. bias related to how a question is posed
7. an interface design approach for complex systems
8. perception of elements, their meaning, and projection of future states
9. type of processing used to resolve ambiguous information
Down
1. when people overtrust automation they become this
2. approximate number of items kept in short term memory
3. law relating response time to number of choices
5. law relating movement time, target size and distance
6. error with wrong intention
