| A controller to provide the sense of touch. |
Conveying Forces to the User |
|
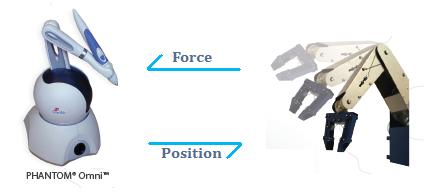
Background Imagine being able to truly feel a video game where you can touch your environment, or imagine feeling what a robot touches. There is research into these types of scenarios under the name "Haptics." Specifically, a user can use a remote control device (called the Master) that works under the same principle as a joystick to control a robot (called the Slave) or manipulate a virtual world.
As the user manipulates the environment or controls a robot, the Master can convey forces to the user that reflects the forces felt by the Slave or the virtual "hand." Applications There are various applications for haptic devices. We touched on the two types: Virtual:
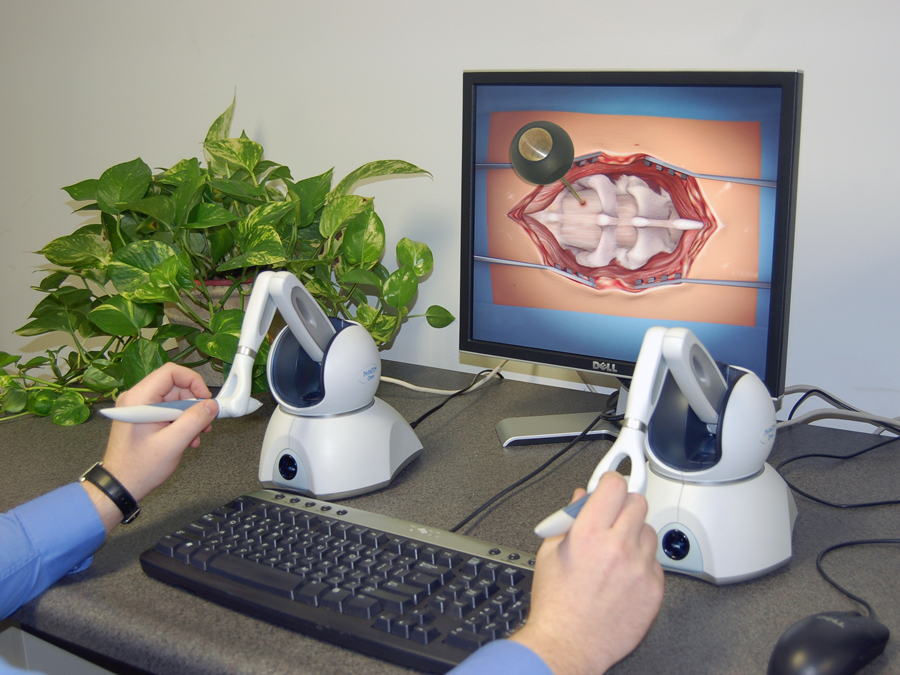
Courtesy SensAble Technologies(sensable.com) Teleoperations:
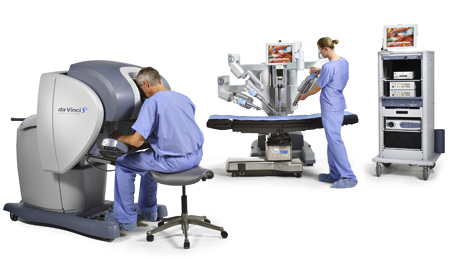
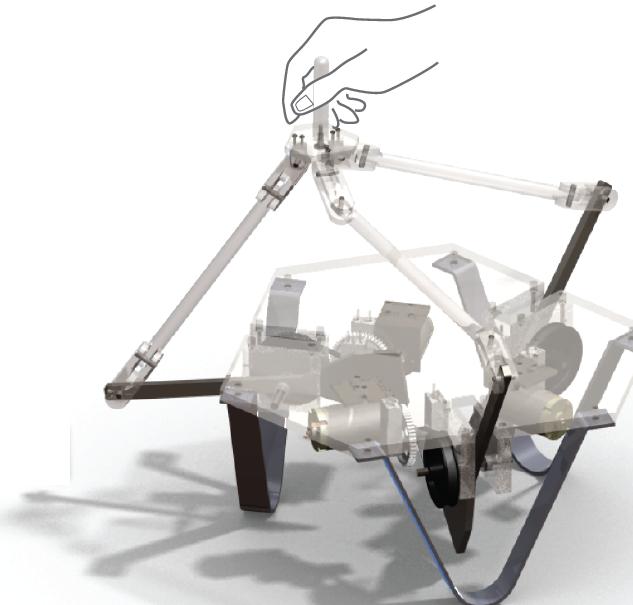
Courtesy Intuitive Surgical (intuitivesurgical.com) The Problem Current commercial products do not provide large workspaces or do not act as stand-alone units that can be easily installed and used. Also, many of the commercial devices only convey small forces so the applications may be limited. There are also many teleoperation applications, such as robotic surgery, that still do not convey force feedback. So for example, the surgeon is not able to "feel" like he or she normally would when operating with surgical tools. This could mean longer training time for surgeons and more importantly, possible difficulty in gauging the forces applied to the patient. Objective Design a Master controller with force feedback in order to provide a sense of touch to the user. In the current circumstances, the Slave robot will be simulated in a virtual environment. |