Soft lithography is mainly composed of two separate techniques: rapid prototyping and replica molding. Rapid prototyping refers to the fabrication of a master with positive relief microchannel structures using photolithography with inexpensive high resolution transparency masks. In replica molding, an elastomer material such as poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) is cast against the master producing a replica containing the imprinted microchannel network. The mold is then bonded to another substrate to complete the microchannel network. The general fabrication process is outlined in the figure below.
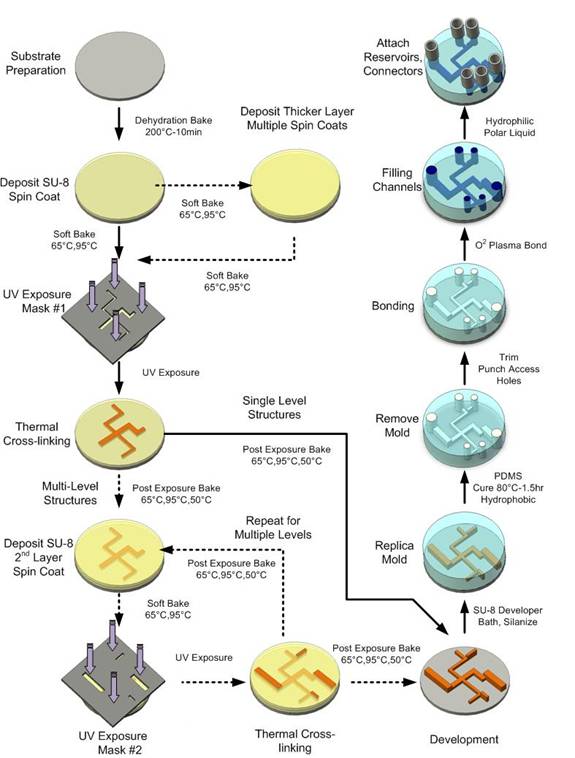
As part of my Masters work I helped develop the protocols and setup the equipment for fabricating PDMS chips. This involved determing the appropriate calibration curves for spin speed vs. thickness, exposure times, UV filter requirements, bake times, and plasma bonding conditions. Procedures for attaching inexpensive Luer fluidic connectors to the chip were also developed.
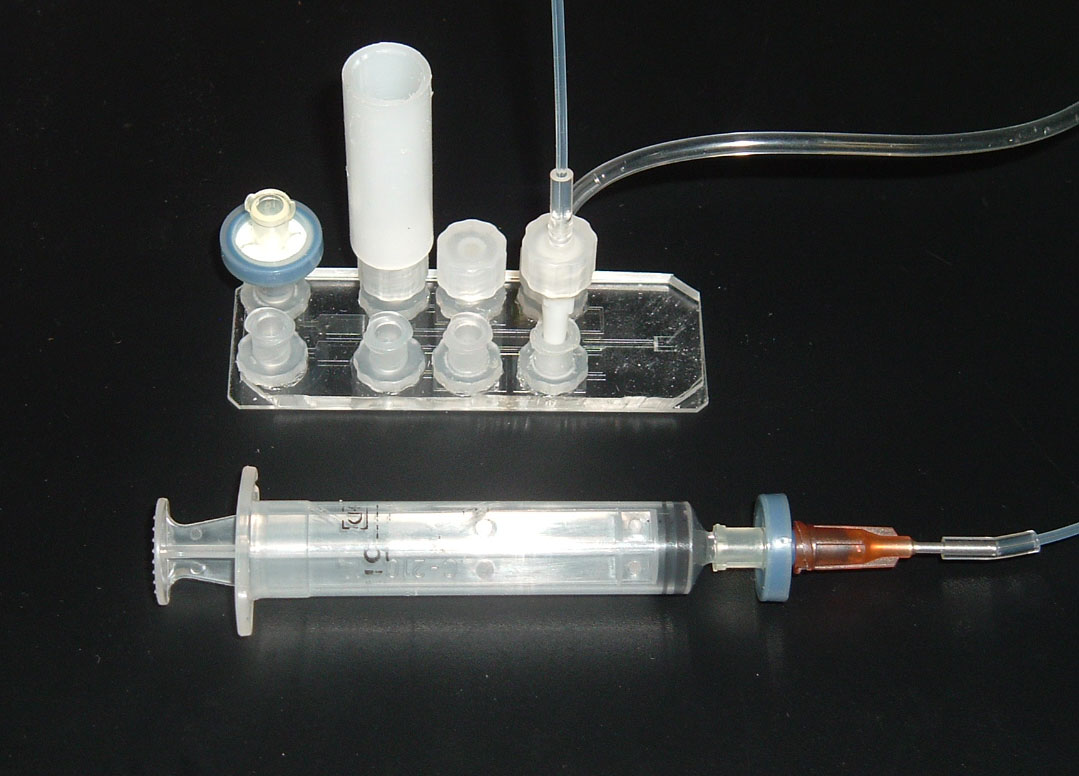
For more information on this work please refer to Chapter 5 in the following publication: